| Incremental Quantity Based Pricing
Per Product Incremental quantity based pricing per product sets the price
of one product based upon either the total quantity of that product OR
the total quantity of all products in the basket. Instead of applying one
price based upon the total quantity, a different price may be applied to each
quantity range. The following examples illustrate how incremental quantity
based pricing is a more compelling incentive and provides more control over profit
margins at each volume incentive level. Example 1: Simple Quantity Based
Price Discount
Customer receives a 20% discount on all when ordering more
than 3. Qty | Price
Each | Amount | Cost
Each | Total Cost | Profit
$ | Profit % | 1 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 50
% | 2 | 5.00 | 10.00 | 2.50 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 50
% | 3 | 5.00 | 15.00 | 2.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 | 50
% | 4 | 4.00 | 16.00 | 2.50 | 10.00 | 6.00 | 38
% | 5 | 4.00 | 20.00 | 2.50 | 12.50 | 7.50 | 38
% | 6 | 4.00 | 24.00 | 2.50 | 15.00 | 9.00 | 38 % |
Above
is an example of a simple quantity based discount. Notice that when than 3 or
more are purchased all of the products are priced at $4.00. With
Incremental Quantity Based Pricing the first 3 products are still priced
at the initial value while the next level of pricing is charged in addition to
the price of the first 3 products. Below is an example.
Example 2:
Incremental Quantity Based Pricing
Customer receives a 20% discount
on quantities above 3. 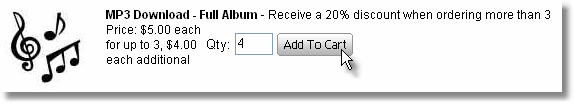

Qty | Price
Each | Amount | Cost
Each | Total Cost | Profit
$ | Profit % | 1 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 50
% | 2 | 5.00 | 10.00 | 2.50 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 50
% | 3 | 5.00 | 15.00 | 2.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 | 50
% | 4 | 4.00 | *19.00 | 2.50 | 10.00 | 9.00 | 47
% | 5 | 4.00 | **23.00 | 2.50 | 12.50 | 10.50 | 46
% | | | *(3
at $5 each plus 1 at $4.00 each)
**(3 at $5 each plus 2 at $4.00 each) | | |
In
the example above you will notice that when the customer purchases more than 3
of the product(s) they are charged the $5.00 initial price for the first 3 and
the $4.00 discounted price for any amount of the product(s) in addition to the
first 3. The profit margin is greater than a simple quantity based pricing feature. Example
3: Incremental Quantity Based Pricing
Customer receives a 30% discount
on quantities above 3.
Qty | Price
Each | Amount | Cost
Each | Total Cost | Profit
$ | Profit % | 1 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 50
% | 2 | 5.00 | 10.00 | 2.50 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 50
% | 3 | 5.00 | 15.00 | 2.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 | 50
% | 4 | 3.50 | *18.50 | 2.50 | 10.00 | 8.50 | 46
% | 5 | 3.50 | **22.00 | 2.50 | 12.50 | 9.50 | 43
% | | | | *(3
at $5 each plus 1 at $3.50 each)
**(3 at $5 each plus 2 at $3.50 each) | | |
Notice
that even though the customer is receiving a greater discount on the product(s),
when purchasing more than 3, you would still have a greater profit margin than
if you were using a simple quantity based pricing as displayed in example 1. This
is because the products on the first pricing level, in this example 1-3, are still
charged at the initial price of the product.
Price Based
Upon Quantity Of All Products In The Basket Incremental quantity based pricing
for ONE product may alternatively be based upon the quantity of ALL products
in the basket. When quantity of all products is applied, the same price levels
apply to the product that the pricing is set for. The only difference is that
the quantity base pricing is based upon the quantity of all products instead of
only the quantity of the one product that the price levels are set for. See
Also: Incremental
Quantity Based Pricing Per Product - Help Topic Tech
Tips Index | 
